Poker Hands Betting Strategy
By Alton Hardin
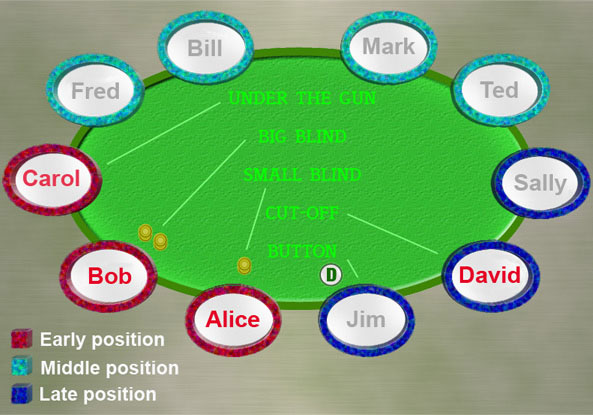
Reading poker articles, playing around with poker tools, and talking over hands with friends are a few of the many ways you can improve your game away from the table. Tip #8: Do you know definitively whether your river bet is a value bet or bluff? In the poker chart below you see K-7 suited (suited = two cards of the same color, i.e. 3 of hearts and 7 of hearts) and you see that this hand can be played in late or middle position. Since you are the 6th player to the left of the dealer button, you are in middle position and can therefore play the hand. What hands are rank highest in Poker. Sports Betting Poker 100% up to $1,000 NLOP Free., CardPlayer has provided poker players with poker strategy, poker news.
- Our positional advantage in the hand. This short poker strategy article on 3-betting 101 covered the basics behind 3-betting and linear versus polarized 3-betting ranges. While this article is far from being a comprehensive 3-betting strategy guide, it should help guide beginners in the right direction with their 3-betting game.
- Poker revolves around betting. Betting in poker can serve several functions and betting patterns in poker can be very complex. This certainly holds true in no limit games in which you cannot only decide whether to bet or not, but are also free to bet whatever amount you wish to.
Introduction
For beginners, 3-betting can be a confusing concept to understand and properly apply at the poker tables. With so much theory being discussed in books, forums, and training videos its easy for beginners to get lost in a fog of poker haze, not knowing when to 3-bet, what range of hands to 3-bet and why. The purpose of this article is to provide a basic framework that beginning and struggling poker players can use to effectively 3-bet.
What Is The Pre-Flop 3-Bet?
First off, lets level set what a pre-flop 3-bet is. A 3-bet occurs when someone open-raises and another person re-raises pre-flop. The re-raise is a 3-bet. This might be a bit confusing to some people because the 3-bet is the second raise, why is this? Well, in Texas Holdem the posted blinds are considered the first bet, the initial open raise is considered the second bet, and the re-raise is therefore the third bet, hence the term 3-bet.
Linear and Polarized 3-Bets
In poker, there are two main categories of 3-bets, linear and polarized 3-bets:
Linear 3-Betting Range
Poker Hands Betting Strategy Tactics
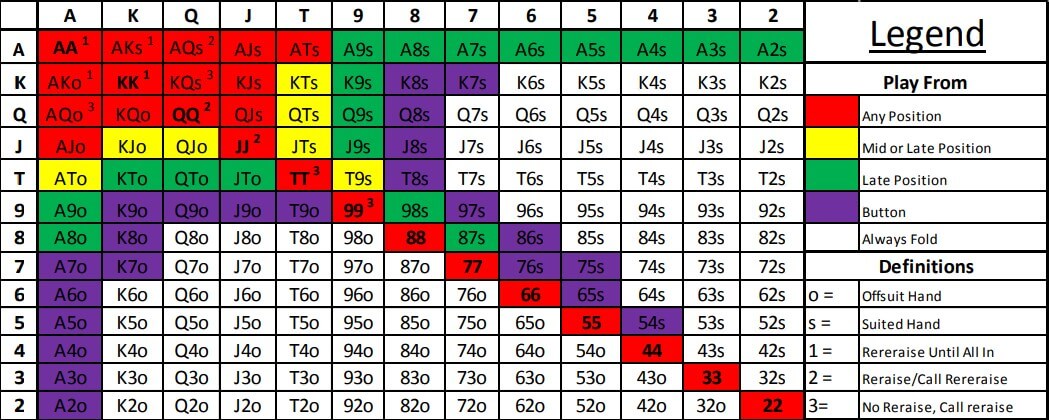
A linear 3-betting range is one composed solely of value-bets. When we 3-bet a linear range, we are 3-betting for value. For example, the image below shows a linear value 3-betting range of JJ+, AQs+, AKo.
Polarized 3-Betting Range
A polarized 3-betting range is one composed of a combination of value hands and bluffs. So, unlike the linear 3-betting range, when we 3-bet a polarized range, we are sometimes betting for value and other times bluffing. The below image shows a polarized 3-betting range composed of value hands and bluff hands. In this example, we are 3-betting TT+, AJs+, AQ+ for value and 44-22, A4s-A2s, 87s, 76s as a bluff.
Why Do We 3-Bet?
Hopefully you’ve already noticed this from the section above, but we 3-bet for two specific reasons:
- When we have a hand that is too good to call, such as KK or AA for value
- When we have a hand that is too bad to call, such as A2s or 33
If we have a hand that fits within these two different reasons, then we have a hand we can “potentially” 3-bet.
Linear or Polarized?
So which should you use, the linear or polarized 3-betting model? It depends on our opponents.
Can We 3-Bet Bluff?

You probably heard the phrase, “never bluff the calling station”. Well the same goes for 3-bets. You should only apply the polarized 3-betting model with 3-bet bluffs if your opponent(s) are folding to a lot of 3-bets. If they aren’t, then 3-bet bluffing will only cause you to unnecessarily spew off a lot of chips pre-flop. Conversely, if your opponent(s) are folding to a high frequency of 3-bets, approximately 67% then you can 3-bet bluff profitably.
Therefore, 3-bet bluffing and the polarized 3-betting model works best when you have a lot of fold equity. When your fold equity is low, don’t apply this model and stick with the linear 3-betting model.
Poker Hands Betting Strategy Games
How Wide Should We Value 3-Bet Bet?
Again, this is dependent upon how your opponent(s) are reacting to 3-bets. When you are 3-betting for value, the most important factor is your opponent’s 3-bet calling range and 4-betting range.
When you are 3-betting for value, you goal is to maximize your long-term expectation in the hand by having your opponents call your 3-bet with worse hands. For example, if your opponent is folding to 100% of 3-bets (this isn’t really realistic but proves a point), then it does you no good to 3-bet KK or AA. Against this specific opponent it is more profitable to flat his or her pre-flop raise. Conversely, if your opponent is folding to next to no 3-bets, then it is highly profitable to 3-bet a very wide range for value!
So here are some general guidelines on 3-betting for value:
- Always adjust your 3-bet value range to how your opponents react to 3-bets
- Consider your opponent’s 3-bet flatting range and 4-betting range
- The less your opponent is folding to 3-bets, the more you can widen your value range
Low versus High Fold Equity
Therefore, if you have high fold equity you should employ the polarized model. If you have low fold equity, use the linear 3-betting model.
3-Bet Sizing
When sizing your 3-bets, I recommend beginner start with the 3x rule: raise three times your opponents initial open raise sizing.
- When you are out of position to the raiser, make your sizing a bit more, closer to 3.5x. Why? Our positional disadvantage in the hand.
- When you are in position to the raiser, make you sizing a bit less, closer to 2.8x. Why? Our positional advantage in the hand.
Summing Up
This short poker strategy article on 3-betting 101 covered the basics behind 3-betting and linear versus polarized 3-betting ranges. While this article is far from being a comprehensive 3-betting strategy guide, it should help guide beginners in the right direction with their 3-betting game.
For a more comprehensive overview of 3-betting, be sure to watch our The Three-Betting 101 Course!
Poker revolves around betting. Betting in poker can serve several functions and betting patterns in poker can be very complex. This certainly holds true in no limit games in which you cannot only decide whether to bet or not, but are also free to bet whatever amount you wish to.
Beginning players often aren't aware of the reason why they bet, let alone the best amount they could bet in certain situations. A lot of beginning poker players as a result make big mistakes with their betting strategy and for that reason alone might find themselves losing their money on a structural basis. This article is meant to give you a basic understanding of when you should bet how much and what for; to teach you a basic no limit hold'em betting strategy.
Contents of this betting strategy guide:
Reasons for betting in poker
Besides betting because you feel like it or because it gives you a nice round figure in your chip stack there are several other reasons for betting in poker. The most common reasons for betting are the following:
- Betting to get value for your good hands
- Betting as a bluff
There are also several other reasons why poker players tend to bet, but which are more or less a form of one of the two reasons mentioned above:
- Betting for protection
- Betting for information
- Betting to gain the initiative
- Block betting
The correct amount to bet in a certain situation often depends on the reason why you are betting. This will become clear in the following section where all the above mentioned reasons for betting in poker are discussed separately.
Value betting in poker
Value betting is betting with what you think will be the best hand. If you are value betting your hand, then you hope to get called by your opponent holding a worse hand than yours.
Note that you can only make an estimation of a range of hands your opponent is likely to hold. So, to be more specific, you are value betting your hand when you think it is ahead of your opponent's range of hands. Even if you get called by a hand in the top of your opponent's range that has you beat, you are value betting.
When you want to bet for value the trick is to bet an amount that wins you the most: you don't want to bet too much and scare your opponent off, but you don't want to bet too little and miss out on the money your opponent would have called more with his or her inferior hand either. Therefore it is very important to read your opponents well; to think about the hands your opponents could have and how much they would be willing to call with those hands.
In addition you could also use your bet sizing as a tool to be deceptive to your opponent and to lure your opponent into making big mistakes. An example would be inducing a bluff raise which is further explained in the section specifically about bet sizing.
Betting as a bluff
Bluffing in poker is betting with what you think will not be the best hand at showdown. If you are bluffing then you don't want your bet to be called by your opponent.
Bluffing is basically saying to your opponent that your hand is the better one and that he or she should fold. It is very important in order to bluff successfully and to not be a big donator of chips instead that your story adds up. In addition your opponent has to pick up on this story and he or she should be capable of laying down a second best hand.
The reason that bluffing at the lower stakes is not recommended is that you are mostly dealing with opponents who are not aware of you telling a story to them and who are incapable of laying down hands. You could make the most elaborate and sophisticated bluff in the world, but if you are dealing with such opponents then this bluff will be nothing more then spew or 'fancy play syndrome'.
If you want to bluff, the trick when it comes to bet sizing is to get the job done with as little chips as possible while still keeping up the story of you having a big hand. You don't want to risk more then necessary and you need to be credible. The more you bet as a bluff, the more often your bluff has to work in order to be profitable.
You can also semi-bluff in poker. This is betting when you hold a draw like a flush or a straight draw. This kind of bluff has several advantages: you could pick up the pot right there with your semi-bluff; it disguises your draw; if you get called then you have outs and it helps you build the pot for when you do hit your draw.
Betting for protection
Betting for protection is essentially a form of value betting your hand. By betting for protection you deny your opponents a free card that could give them a better hand when they are drawing.
When you are betting with the intention to protect your made hand against draws there is a minimum amount you have to bet in order to let your opponent make a mistake when he or she decides to continue with the hand. If you bet too little, then you give your opponent the right pot odds to call and try to outdraw you. Note that you can't make your opponent fold a hand. You can only make sure that (s)he makes a mistake when continuing with the hand.
Betting to gain initiative
Betting in poker is seen as an act of aggression. It gives you momentum: other players will have to make at least a decent hand or otherwise collect the nerves to bluff their way out if they want to continue when you keep on betting. Betting to gain initiative and to exploit this initiative (as with a continuation bet) is therefore essentially a form of bluffing as you don't fully rely on the strength of your hands. Although bluffing at the low stakes poker games is not recommended, betting to gain initiative and continuation betting on the flop are very important strategies to incorporate into your game.
Betting for information
Betting for information is probably one of the vaguest reasons you could bet for, yet it is often mentioned by poker players. The problem with betting for information is that when your bet for information just gets called this often doesn't tell you a whole lot about your opponent's hand. At the same time however, the pot is getting bigger and bigger while your hand probably isn't very strong (otherwise you would have just been betting for value). Betting for information is therefore not a very good reason to bet and you might be better of to just check instead.
Block betting
Betting to block is betting when you are first to act with the intention to set the price. This is usually done with weaker hands when players aren't sure whether their hand is good or not. They don't want to call a big bet by their opponent if they check to him and therefore they bet a smallish amount themselves (and hope to not get raised). It can be a valid betting strategy as you get some value from weaker hands and possibly lose less against stronger hands.
Paying attention to bet sizing: how much to bet in poker?
A key concept when it comes to betting in poker is that you should size your bets in relation to the total pot size (just like you should view your opponent's bets relative to the size of the pot). This is very important, because the bet size relative to the pot size determines the pot odds that you give your opponents. A very common range for bet sizes is anywhere between 50-100% the size of the pot.
Another important thing to keep in mind is to not vary your bet sizing based on the strength of your hand. If you would do this, other players might notice and get a 'tell' on you. They will see that you are betting strong only with your big hands and avoid paying you off. Or they might notice that you are betting small with your weak hands or bluffs and push you off of your hands.
Bet sizing when betting for value or as a bluff
When you are purely betting for value or as a bluff then you are very free in your bet sizing. As already mentioned, the trick with valuebetting is to bet an amount that wins you the most. This does not necessarily have to be the amount that gets called the most.
As a general rule betting larger against very loose opponents who don't like to lay down their hands will be more profitable. And because at the lower stakes online cash games you will encounter a lot of those opponents it is very important that you bet strong when you are very likely or even sure to be ahead. Strong betting means that you should be betting around 75% of the pot or even more. You could sometimes consider slowing down a bit when the board is unlikely to have hit your opponent and you are holding a monster like top set or bigger yourself. This should be an exception though.
Example 2: Again you're on the river with the nuts, the same pot size and the same stacks as in the previous example. This time you suspect your opponent might have a missed draw and you also know that your opponent is very aggressive and likes to bluff people of their weak hands. Now you could decide to bet less, say $1.65, to make it look like you are weak and induce a bluff raise by your opponent.A good thinking player however might see your smaller bet as strength: it looks like you are begging for a call, so you must have a strong hand. In this case a normal or even a large bet size would probably be better. You could save the smaller bet size against this opponent as a bluff.
If your opponent really thinks things through and knows you know him and vice versa, then he could be thinking that you know that he knows that the small bet size would mean strength and are therefore using it as a bluff. Now this could again lure him into calling with very weak hands or he could even bluff raise you. This 'I know that you know' thing is called multiple level thinking. I told you betting can be very complex, isn't poker a fun game? Multiple level thinking is not something you'll have to worry about at the micro stakes very often though.If you flop a really big hand then you should look for a way to get your whole stack in the middle on the river without making any huge oversized bets at any point in the hand. You would want to avoid betting too small on the flop and the turn and having to bet 1.5 times the pot on the river to get it all-in. It is important to plan your bet sizing over multiple streets of betting.
And now for some bluffing:
Of course you won't be able to calculate all those percentages in the heat of battle, just like you won't be able to calculate exact pot odds and odds of hitting your draws and winning versus a certain hand range. The above examples are meant to give you an idea what you should roughly be thinking about when determining how much to valuebet or bluff. You can save the exact calculations for when you want to analyze your plays accurately away from the poker table.
Bet sizing when betting for protection
The common bet size of 50-100% of the pot also happens to be the correct amount to bet for protection if your opponent could hold potential flush or straight draws. It is advisable to bet closer to 100% the size of the full pot in this case, certainly against opponents who like to chase their draws. This way they will be making bigger mistakes by calling, which means more profit for you in the long run. If you're unsure about why this is a correct amount to bet versus potential flush or straight draws I'd advise you to read the pot odds guide. You'll see that this bet size will deny your opponents the proper pot odds to call with draws that have up to 15 outs.
Of course your opponent will not always have the straight or the flush draw when the board offers this potential with two cards to a straight or a flush. But because you don't know when they do or when they don't have the draw, it is best to just assume they always have it. This way you will never give away free cards where you could have gotten a lot of value from a draw instead.
Pre-flop raise sizing
If you decide to play a hand and you are the first to act before the flop then you might already know by now that raising is generally preferable over limping (just calling the big blind). Raising gives you initiative and it tends to weed out the very weak starting hands. On top of that it will result in getting more value for your good hands.
The general rule of thumb here is to raise 3 or 4 times the big blind and add one big blind for every limper. So if there are two players in front of you just calling the big blind and you find a nice hand like AQ you should raise to 5 or 6 times the big blind. If you raise less, then it will be too attractive for all kinds of hands to come along and take a look at the flop. If you raise more, then you are unlikely to get any action by worse hands at all. If you are dealing with particularly loose opponents, such as at the nano and micro stakes, then raising a little bit more pre-flop could be a valid strategy.
Common mistakes in a beginner's no limit hold'em betting strategy
Below is a list of the five most common betting strategy mistakes seen at the no limit hold'em micro stakes cash games.
Calling too much instead of betting and raising
Aggression, or rather controlled and selective aggression, is important in no limit hold'em. If you are not aggressive enough, which is characterized by calling a lot instead of betting and raising, you let your opponents outdraw you cheaply. You also won't get enough value for your big hands and you will generally get less information about the strength of your opponent's hands and therefore of where you stand in a hand.Betting and raising too small
If you only make minimum bets and raises then you are just inviting players to enter the pot and take a shot at cracking your monster hands. Always think of the pot odds you are offering your opponents. In order to let your opponents make mistakes when they want to draw out on you, you have to bet strong: around ¾ the size of the pot will do fine as a general rule of thumb.Betting and raising too big
This one is actually pretty funny to witness: a very tight player suddenly wakes up and comes in raising 6 or 7 times the big blind pre-flop or reraises someone else's raise by a ridiculous amount of 5 times or more. You have to be really oblivious as an opponent to not have all your alarm bells going off at the same time that you are either facing queens, kings or aces and maybe, just maybe AK. I don't know whether it is the fear to play poker after the flop and to get outdrawn or impatience of getting all the money in the pot with a great hand. I do know that this kind of betting strategy will only scare the majority of opponents off and won't result in becoming a tough and unpredictable player to play against.Betting without a plan
You should always have a clear idea of what you want to accomplish with your bets and always ask yourself if betting in fact does accomplish what you had in mind. In addition you should start to make a plan early in the hand for several scenarios later in the hand. Think about the possible reasons for betting in poker. Do you want to get value? Do you need to protect your hand against one or more possible draws? How much should you bet now and on the turn to get all-in on the river without having to bet a weird large amount? What will you do if your bet gets raised? And what if the possible draw hits? Does betting as a bluff make sense here at all considering what my opponent thinks that I could have based on the betting in previous rounds?Betting for value when no worse hands will call
This is basically an example of betting without a plan or betting without thinking about what betting will accomplish. Say you get to the river where you hold a top pair and the board shows four cards to a straight and three cards to a flush and your opponent checks to you. Okay, so your opponent might be weak because he checks, but betting wouldn't really accomplish anything here. You are unlikely to fold out better hands and worse hands are probably not going to call. So a bet will only lose you more money when you are behind and will probably win you the same amount if you are ahead. And that's not what defines a good bet.
Betting in poker - conclusion to this betting strategy guide
I hope that this article has helped you to see what you can achieve with your betting in poker. Betting is much more than just throwing chips in the pot; it can serve several important purposes. Let's conclude with an overview of some take home messages:
- Always bet for a reason. Have a plan for the rest of the hand.
- Always see bet sizes in relation to the pot size. Common bet sizes are between 50-100% of the pot. Bet closer to a 100% of the pot if you want to bet strong.
- Before the flop a raise size of 3 or 4 big blinds plus one big blind for every limper in front of you is a very good starting point.
- Don't vary your bet sizing based on the strength of your hand.
- Selective aggression and choosing the right bet size will help you to protect your hands and to get value from weaker hands.
- There is very little to no need for pure bluffing at the lower stakes if you make sure you get enough value for your strong hands. You can generally bet bigger for value against very loose opponents.
- Always try to think of how your opponent might perceive your betting pattern.

These pointers form the big picture when it comes to betting in poker. If you follow them and try to implement them in your game, then you will likely become a player to be reckoned with at the table. Don't worry about betting specific plays like check-raising, squeezing and isolating yet. These 'details' will come when you have the basic foundation right.
Further reading at First Time Poker Player:
Further reading across the internet:
- The Poker Bank - Bet Sizing in No Limit Poker
- Tight Poker - Value Betting - Advanced Strategy in Extraction
- Poker-Strategy.org - Online Poker Bluffing
- Noted Poker Authority - Betting For Value Versus Inducing A Bluff